The Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Storage Solutions highlight a transformative shift in how we store and manage data in today’s digital age. With the proliferation of cloud technology, individuals and businesses alike are embracing the convenience and flexibility it offers. Cloud storage is not just about storing files; it encompasses various models, including public, private, and hybrid options, each with its unique features and benefits that cater to diverse needs.
As we dive deeper, we’ll explore the significant advantages that cloud storage brings, such as cost-effectiveness and enhanced collaboration, while also addressing the challenges like security risks and internet dependency. Understanding these elements is crucial for making informed decisions about adopting cloud solutions in personal and professional settings.
Overview of Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud storage has transformed the way individuals and businesses manage their data. By utilizing remote servers accessible via the internet, cloud storage allows users to store, retrieve, and manage files without the need for physical hardware. This flexibility and accessibility make cloud storage an essential component of modern IT infrastructure.Cloud storage primarily functions by allowing data to be stored on remote servers managed by service providers.
Users can access this data anytime, from anywhere, using various devices. The technology operates on a multi-tenant architecture, meaning multiple users can share the same resources while maintaining their individual privacy and data integrity.
Models of Cloud Storage
Understanding the different models of cloud storage is crucial for selecting the right solution based on your needs. There are three primary models: public, private, and hybrid.
- Public Cloud Storage: Offered by third-party providers, public cloud storage allows multiple users to share the same infrastructure. It is usually cost-effective, as users only pay for the storage they use. Notable providers include Amazon S3, Google Drive, and Microsoft OneDrive.
- Private Cloud Storage: This model is dedicated to a single organization, providing more control and security. A private cloud can be hosted on-premises or in a data center, suited for businesses that handle sensitive data. Examples include VMware vCloud and Microsoft Azure Stack.
- Hybrid Cloud Storage: Combining both public and private cloud solutions, hybrid storage offers flexibility and scalability. Organizations can store sensitive data in a private cloud while leveraging the public cloud for less critical information. This approach balances security needs with cost-effectiveness.
Popular Cloud Storage Providers and Their Features, The Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Storage Solutions
The market is filled with various cloud storage providers, each offering unique features tailored to different user needs. Here is a list of popular options:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Known for its extensive range of services, AWS provides scalable storage solutions like Amazon S3, which offers high durability and availability.
- Google Drive: With seamless integration into the Google Workspace ecosystem, Google Drive allows easy collaboration and sharing, making it ideal for teams.
- Microsoft OneDrive: Integrated with Microsoft 365, OneDrive provides excellent collaboration tools and security features, suitable for both individual and enterprise users.
- Dropbox: Focused on simplicity and user-friendly design, Dropbox is popular for its file synchronization capabilities and strong sharing features.
- Box: Aimed at businesses, Box emphasizes security, collaboration, and integration with various productivity tools, making it suitable for enterprise-level storage needs.
Benefits of Cloud Storage
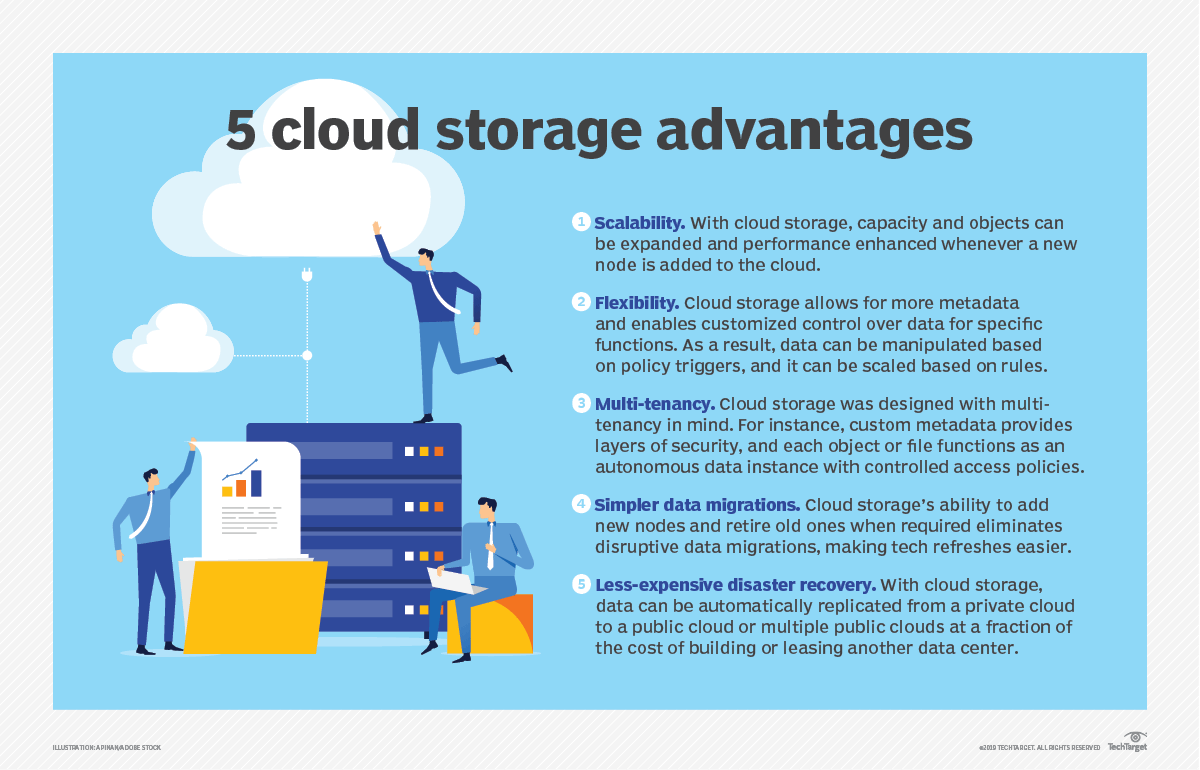
Cloud storage solutions offer a range of advantages for both individuals and businesses, revolutionizing the way data is stored, accessed, and managed. These benefits stem from the flexibility, scalability, and efficiency that cloud storage provides, making it an attractive option compared to traditional storage methods.One of the standout advantages of cloud storage is its cost-effectiveness. Unlike traditional storage solutions that often require significant upfront investments in hardware and maintenance, cloud storage operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to pay only for the space they need.
This reduces capital expenses and mitigates the financial risks associated with over-provisioning storage resources. Businesses can scale their storage needs up or down based on demand without incurring hefty costs for unused capacity.
Cost-Effectiveness of Cloud Storage
Understanding the financial implications of adopting cloud storage is essential, especially when comparing it to traditional methods. Here are a few key points to consider regarding the cost-effectiveness of cloud storage:
- No Hardware Costs: Cloud storage eliminates the need for purchasing and maintaining physical servers or storage devices. This not only saves money but also reduces the burden of hardware management.
- Reduced IT Staffing Needs: With cloud storage solutions, the requirement for extensive IT staff to manage physical infrastructure can be significantly reduced, leading to further cost savings.
- Scalability: Users can quickly increase or decrease storage capacity based on their current requirements, allowing for optimal resource utilization without unnecessary spending.
- Disaster Recovery: Many cloud storage providers include backup and recovery solutions as part of their services, minimizing the financial impact of data loss incidents.
The flexibility of cloud storage enables businesses to allocate resources more efficiently, resulting in long-term savings.
Collaboration Enhancement Through Cloud Storage
Cloud storage not only aids in efficient data management but also plays a crucial role in enhancing collaboration among teams. The ability to access and share files from any location fosters a more connected work environment. Consider the following benefits of cloud storage in terms of collaboration:
- Real-Time Collaboration: Teams can work on documents simultaneously, with changes reflected instantly. This leads to improved productivity and creativity, as multiple individuals can contribute to a project without the hassle of version control issues.
- Access from Anywhere: Whether working from home, a coffee shop, or during business travel, employees can access critical files and data from any device with an internet connection, ensuring continuity of work.
- Centrally Stored Information: Cloud storage centralizes data, making it easier for team members to find and utilize necessary information without diving into disparate systems or locations.
- Enhanced Security Features: Many cloud storage providers offer advanced security protocols, which can protect sensitive information while allowing authorized team members easy access.
The collaborative features of cloud storage empower teams to work more effectively, driving innovation and improving overall performance.
Challenges of Cloud Storage
Despite its numerous benefits, cloud storage solutions come with their own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for organizations to make informed decisions regarding their data management strategies. The following sections will explore security risks, internet dependency, and the varying challenges faced by small businesses compared to large enterprises.
Potential Security Risks Associated with Cloud Storage
Cloud storage systems are not immune to security threats, making data protection a top concern for users. Security risks include data breaches, unauthorized access, and loss of data integrity. When sensitive information is stored in the cloud, organizations must consider potential threats from cybercriminals who may exploit vulnerabilities in the infrastructure. A significant concern is the risk of data breaches, which can occur due to inadequate security measures by the cloud provider or human error during data handling.
Encrypted storage and secure access protocols can mitigate these risks, but they do not eliminate them entirely. Organizations must assess the security certifications and compliance standards of their chosen cloud provider to ensure robust protection.
“A data breach can lead to costly consequences, both financially and in terms of reputation.”
Limitations Related to Internet Dependency for Accessing Cloud Storage
Cloud storage solutions inherently rely on internet connectivity, which can present challenges for users. Accessing data stored in the cloud requires a stable and high-speed internet connection. This dependency means that disruptions in service can hinder productivity and data accessibility, particularly in areas with unreliable internet infrastructure.Moreover, latency issues can arise when large files need to be uploaded or downloaded, affecting workflow efficiency.
Organizations should have contingency plans in place to manage situations where internet access is limited or non-existent, which could include maintaining local backups or redundant connectivity options.
Challenges Faced by Small Businesses Versus Large Enterprises
The hurdles associated with adopting cloud storage solutions can differ significantly between small businesses and large enterprises. Small businesses often face budgetary constraints that limit their ability to invest in comprehensive cloud solutions. They may struggle with understanding the full range of services available and choosing the right provider that offers both affordability and security.In contrast, large enterprises typically have the resources to invest in more advanced cloud infrastructure but face challenges related to the integration of cloud solutions with existing systems.
They must also manage complex compliance requirements and data governance policies that can be resource-intensive. The following points highlight these differences in challenges:
- Small businesses may lack the expertise to effectively manage cloud solutions, leading to inefficiencies.
- Large enterprises deal with data fragmentation due to the integration of cloud services across multiple departments.
- Cost considerations for small businesses can limit the scalability of cloud solutions.
- Large enterprises face the risk of vendor lock-in, making transitions to new providers complicated.
Understanding these challenges enables businesses of all sizes to create strategies tailored to their specific needs and limitations, ensuring a more effective approach to cloud storage adoption.
Security Measures in Cloud Storage: The Benefits And Challenges Of Cloud Storage Solutions
Ensuring the security of data stored in the cloud is paramount for both individuals and organizations. With increasing reliance on cloud storage solutions, understanding the best practices for securing sensitive information is essential to mitigate risks and protect data integrity. Effective security measures not only safeguard data from unauthorized access but also help in maintaining compliance with various regulatory frameworks.A comprehensive approach to securing data in cloud storage involves several best practices, each playing a crucial role in creating a robust security posture.
By implementing these strategies, users can significantly reduce the chances of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Best Practices for Securing Data in Cloud Storage
To effectively protect data in cloud environments, it’s important to adopt a multi-layered security strategy. The following measures should be considered:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is vital. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption keys.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls by using role-based access management. Ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of exposure.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities. Addressing these weaknesses promptly helps in maintaining a secure environment.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Employ MFA for an additional layer of security during user login, making it more difficult for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Data Backup: Regularly back up data stored in the cloud to recover from potential data loss due to cyberattacks or natural disasters.
Adopting these practices can lead to a more secure cloud storage environment, protecting against threats that could compromise sensitive data.
Choosing Secure Cloud Storage Options
Selecting a secure cloud storage provider is critical. Factors to consider when evaluating cloud storage options include:
- Compliance Standards: Ensure the provider adheres to relevant compliance frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS, depending on your industry needs.
- Reputation and Reviews: Research the provider’s reputation. Look for reviews and testimonials that highlight their security measures and track record in data protection.
- Security Features: Assess the security features offered by the provider, such as encryption protocols, access management tools, and incident response capabilities.
- Data Location: Understand where your data will be stored. Complying with local laws regarding data storage can be crucial for legal and privacy reasons.
These factors can guide users in selecting a cloud storage provider that prioritizes security.
Comparison of Encryption Standards Used by Various Cloud Providers
Understanding the encryption standards employed by different cloud providers can help users make informed decisions. Below is a table comparing the encryption methods used by some popular cloud storage solutions:
| Cloud Provider | Encryption At Rest | Encryption In Transit | Key Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | AES-256 | TLS 1.2 or higher | Customer managed keys or AWS Key Management Service |
| Google Cloud Storage | AES-256 | TLS 1.2 or higher | Google-managed keys or customer-managed keys |
| Microsoft Azure | AES-256 | TLS 1.2 or higher | Azure Key Vault for key management |
| Dropbox | AES-256 | TLS 1.2 or higher | Key management handled by Dropbox |
This comparison highlights the encryption standards each provider uses, aiding users in selecting a secure cloud storage option based on their security needs.
Future Trends in Cloud Storage
As we look ahead, the landscape of cloud storage is poised for significant transformation. Emerging technologies are reshaping how data is stored, accessed, and managed. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into cloud storage solutions is not just a trend; it’s becoming a necessity. These advancements promise to enhance efficiency, security, and user experience in ways we have yet to fully realize.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Cloud Storage
Several technologies are on the brink of revolutionizing cloud storage. Among these, edge computing and quantum computing are particularly noteworthy. Edge computing allows data processing to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. This could enable real-time data analysis and processing in industries like IoT and autonomous vehicles, where immediate access to data is critical.Quantum computing, while still in its infancy, has the potential to change how data encryption and storage are handled, making it possible to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds.
The combination of these technologies with traditional cloud systems can lead to more resilient and flexible storage solutions.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly being incorporated into cloud storage services, leading to smarter data management. These technologies offer several benefits, including:
- Automated Data Management: AI can automate tedious tasks such as data classification and indexing, streamlining workflows for businesses.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms can analyze usage patterns to predict storage needs, helping organizations optimize their resources effectively.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: AI-powered systems can detect anomalies in data access patterns, identifying potential security threats more efficiently than traditional methods.
These advancements allow organizations to manage their data more proactively, reducing risks and increasing operational efficiency.
Shifts in User Demand for Cloud Storage Functionalities
Recognizing the evolving needs of users is crucial in the cloud storage sector. An increasing demand for enhanced security features is evident, as organizations prioritize data protection amid rising cyber threats. Moreover, users are seeking flexible storage solutions that can easily scale with their needs. This includes:
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions: The desire for a blend of on-premises and cloud storage options is growing, allowing businesses to maintain control over sensitive data while leveraging the benefits of the cloud.
- Collaboration Tools: Enhanced functionalities for team collaboration are in high demand, enabling seamless sharing and editing of documents across distributed teams.
- Cost-Efficiency: Users are increasingly looking for pricing models that provide flexibility and transparency, avoiding unexpected charges while maximizing value.
Understanding these shifts is essential for cloud service providers as they develop solutions that align with user expectations and industry trends.
Case Studies of Cloud Storage Implementation
Cloud storage solutions are increasingly being adopted across diverse industries, each tailoring the technology to meet specific operational needs. By examining real-world examples, we can gain insights into the successful integration of these solutions and the challenges faced during implementation.Cloud storage has proven beneficial for numerous organizations, but transitioning to these solutions is not without its hurdles. Below, we explore selected case studies that highlight both achievements and setbacks during cloud storage implementations.
Successful Implementations in Various Industries
Several organizations have successfully implemented cloud storage solutions, leading to significant improvements in their operations. The following examples illustrate the versatility and efficacy of cloud storage across different sectors:
- Netflix: Transitioning to a cloud-based architecture enabled Netflix to handle massive volumes of data and improve content delivery. By utilizing Amazon Web Services (AWS), they achieved a reduction in costs related to infrastructure scaling and enhanced streaming performance, meeting global demand effectively.
- Dropbox: Initially a file-sharing service, Dropbox’s adoption of cloud storage transformed its functionality into a collaborative workspace. This move allowed the company to scale quickly, supporting millions of users without compromising access speed or data integrity.
- General Electric (GE): GE implemented cloud storage to facilitate data collection from its industrial machines in real-time. This shift led to predictive maintenance capabilities, ultimately reducing downtime and operational costs by leveraging data analytics on cloud platforms.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions During Transitions
While many organizations find success, transitioning to cloud storage can reveal several pitfalls. Awareness and proactive management of these challenges can significantly ease the migration process.
- Data Security Concerns: Initial fears regarding data security often hinder organizations from fully embracing cloud storage. Companies like GE invested in robust encryption and access control measures to alleviate these concerns.
- Cost Overruns: Often, projected costs do not align with actual expenses incurred during the transition. Netflix managed this by starting with a pilot phase, allowing them to adjust budgets and resources based on real-time feedback.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many organizations struggle with integrating cloud solutions into existing IT frameworks. Dropbox addressed this by employing API solutions that allowed seamless integration, thereby minimizing disruptions during the transition.
Summary of Key Metrics from Case Studies
The following table summarizes key metrics related to cost savings and efficiency gains from various case studies, illustrating the tangible benefits of cloud storage implementation:
| Company | Cost Savings (%) | Efficiency Gain (%) | Time to Implement (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | 30 | 40 | 6 |
| Dropbox | 20 | 50 | 4 |
| General Electric | 25 | 30 | 12 |
“Transitioning to cloud storage not only streamlines operations but also opens new avenues for data-driven decision-making.”
Industry Expert
Comparison of Cloud Storage Solutions
When selecting a cloud storage solution, businesses need to consider various factors that can affect their operational efficiency and data management. With numerous options available, a thorough comparative analysis can provide clarity and guide informed decision-making. This section will evaluate leading cloud storage providers based on their features, pricing, and user feedback to help organizations identify the best fit for their needs.A comparative analysis of cloud storage providers highlights key differences that can influence business choices.
Below is an overview of notable cloud storage solutions, focusing on established providers like Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive, and Amazon S3.
Comparative Analysis of Leading Cloud Storage Options
This analysis covers essential features, pricing, and user reviews. Recognizing these aspects can aid businesses in selecting a solution that aligns with their requirements.
| Provider | Key Features | Pricing | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Drive | Integration with Google Workspace, file sharing, extensive collaboration tools | Free: 15GB; Paid: Starts at $1.99/month for 100GB | Highly rated for user-friendly interface and collaboration capabilities |
| Dropbox | Smart Sync, file recovery, collaborative tools, third-party app integrations | Free: 2GB; Paid: Starts at $9.99/month for 2TB | Positive reviews for ease of use and file sharing features |
| Microsoft OneDrive | Deep integration with Microsoft Office, file sharing, and version history | Free: 5GB; Paid: Starts at $1.99/month for 100GB | Appreciated for seamless Microsoft Office integration and functionality |
| Amazon S3 | Scalability, high durability, custom security settings | Pay-as-you-go model starting at $0.023 per GB | Well-regarded for flexibility and enterprise-level solutions, though complexity noted |
Understanding the pros and cons of each provider is vital for evaluating options. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages of key cloud storage solutions.
Pros and Cons of Major Cloud Storage Providers
A clear Artikel of the benefits and drawbacks can simplify the decision-making process for businesses. Here is a concise overview. Google Drive:
*Pros
*
Generous free storage space
Excellent collaboration features
- Strong integration with other Google services
Cons
*
Privacy concerns regarding data handling
Limited advanced file management tools
Dropbox:
*Pros
*
User-friendly interface
Strong file recovery options
- Robust third-party integrations
Cons
*
Higher costs for larger storage
Limited free storage capacity
Microsoft OneDrive:
*Pros
*
Seamless integration with Microsoft applications
Advanced sharing options
- Affordable pricing for Office 365 subscribers
Cons
*
Limited offline access features
Can be less intuitive for non-Microsoft users
Amazon S3:
*Pros
*
Highly scalable and flexible
Extensive security and compliance features
- Suitable for large enterprises
Cons
*
Complex setup and management
Costs can add up unexpectedly
Evaluating cloud storage options should involve a structured approach. An effective assessment process includes several key steps:
Evaluation Process for Cloud Storage Options
Conducting a thorough evaluation involves multiple considerations that ensure the chosen solution meets business needs.
1. Identify Business Needs Assess specific storage requirements, including data volume, sharing capabilities, and compliance needs.
2. Research Providers Gather information on various providers by reviewing features, pricing, and customer feedback from reliable sources.
3. Trial Periods Utilize free trials or demo versions to test usability and functionality in real-world scenarios.
4. Security Evaluation Review the security measures offered by each provider, ensuring they meet industry standards and organizational policies.
5. Scalability Consider future growth and whether the provider can accommodate increasing storage demands.
6. Support and Service Evaluate customer support options and response times, which can be crucial when issues arise.By following these steps, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals while ensuring data security and accessibility.