Mobile Wallets vs Credit Cards – Which Is Safer for Online Payments is a question that many consumers are asking in today’s digital age. As technology evolves, the way we handle our finances has transformed dramatically. Mobile wallets offer a convenient alternative to traditional credit cards, but how do they compare in terms of safety? This discussion will delve into the functionalities, security features, and vulnerabilities of both payment methods, guiding you through the essential aspects of online payment security.
We will explore the intricacies of mobile wallets, which utilize features like encryption and biometric authentication, alongside the established protocols found in credit cards. By examining how these technologies function and the challenges they face, we can better understand which option may provide a more secure experience for online transactions.
Overview of Mobile Wallets and Credit Cards
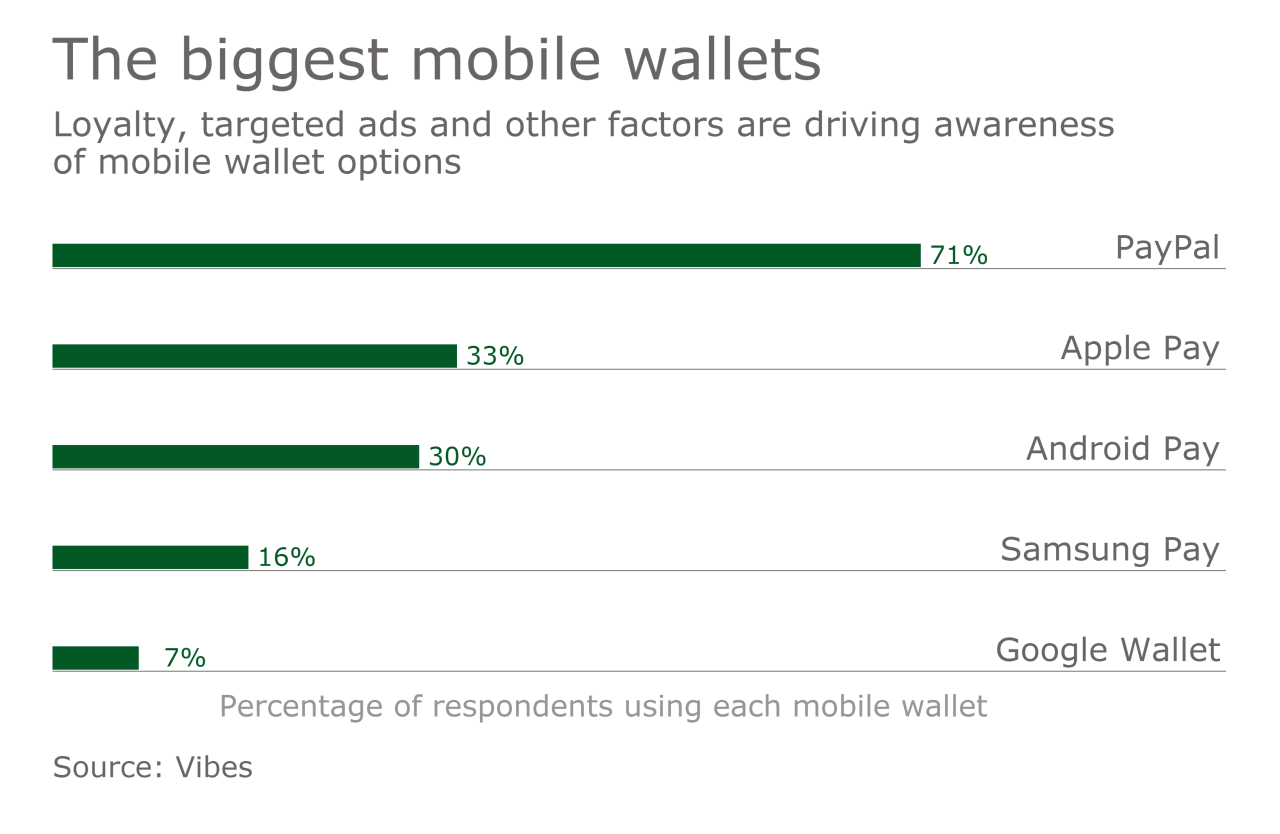
Mobile wallets and credit cards are two prominent methods for facilitating online payments, each with distinct functionalities and benefits. Mobile wallets, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, allow users to store their payment information securely on their smartphones. They provide functionalities like peer-to-peer payments, loyalty program integration, and easy access to transaction history. Credit cards, on the other hand, are physical or virtual cards issued by financial institutions that enable users to borrow funds up to a certain limit for purchases.
They operate based on a credit line, which users repay over time, usually with interest.The evolution of these payment methods has been significant over the years. Mobile wallets emerged as a response to the increasing demand for convenience and security in digital transactions. With the rise of smartphones and advancements in near-field communication (NFC) technology, mobile wallets have gained popularity, allowing users to make quick and secure transactions.
Conversely, credit cards have a long history, dating back to the mid-20th century, evolving from traditional plastic cards to virtual cards used in online payments. Both methods have adapted to changing consumer needs, with mobile wallets integrating features like biometric authentication and credit cards offering enhanced security measures such as EMV chip technology.
Functionalities of Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets offer a variety of functionalities that enhance the user experience in online payments. These functionalities include:
- Secure Storage: Mobile wallets securely store credit and debit card information, reducing the need to enter sensitive data for each transaction.
- Contactless Payments: Utilizing NFC technology, users can make contactless payments at compatible terminals, streamlining the checkout process.
- Loyalty Program Integration: Many mobile wallets allow users to store loyalty cards and earn rewards seamlessly while making purchases.
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Users can easily send money to friends or family through the wallet app, making it convenient for splitting bills or sharing expenses.
- Transaction History: Mobile wallets provide users with access to a comprehensive transaction history, enabling better financial tracking and management.
Operation of Credit Cards in Online Payments
Credit cards function as a line of credit, allowing users to make purchases and pay later. The operation involves several key steps:
- Authorization: When a user makes an online purchase, the merchant sends the transaction details to the credit card issuer for authorization.
- Verification: The issuer verifies the transaction by checking the available credit limit and additional security measures such as the Card Verification Value (CVV).
- Approval or Decline: Based on the verification, the transaction is either approved or declined. An approval allows the merchant to proceed with the order.
- Settlement: Once approved, the funds are transferred from the issuer to the merchant, typically taking a few days to settle completely.
- Billing Cycle: Users receive monthly statements detailing their transactions and the amount due. They can choose to pay the full amount or a minimum payment, which may incur interest charges.
Security Features of Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets have rapidly become a popular choice for online payments, offering convenience and ease of use. However, their security features are what truly make them stand out. Understanding these measures is crucial for users who want to ensure their financial information remains safe.Mobile wallets employ a range of security measures designed to protect user data and transactions. Among these are encryption, biometric authentication, and tokenization, each serving distinct protective roles during the payment process.
Encryption and Biometric Authentication
Encryption is one of the primary security mechanisms used in mobile wallets. It involves converting sensitive data into a coded format that can only be read by authorized parties. Mobile wallets typically use advanced encryption protocols, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), which ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key. Biometric authentication enhances security even further by requiring users to verify their identity through unique biological traits.
This can include fingerprint scanning or facial recognition, providing a layer of protection that is difficult to replicate. For example, Apple Pay utilizes Touch ID and Face ID, allowing only the authorized user to complete transactions, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Tokenization in Mobile Wallet Transactions
Tokenization is another vital aspect of mobile wallet security. This process replaces sensitive card information with a unique token that has no intrinsic value, meaning it cannot be used outside of a specific transaction. When a user makes a payment, the mobile wallet sends this token to the merchant instead of the actual card details. The implications of tokenization are significant; they greatly reduce the chances of fraud.
Even if a hacker intercepts the transaction data, they will only obtain a useless token rather than the actual credit card number. This makes it much harder for fraudulent activities to occur. Major payment networks, such as Visa and MasterCard, have adopted tokenization to enhance transaction security, illustrating its effectiveness in protecting user information.
Security Features of Credit Cards
Credit cards have long been a staple in the world of online payments, and their security features are robust and continually evolving. Understanding these security protocols is essential for anyone who uses credit cards for transactions, as they help protect against fraud and unauthorized use.One of the key security protocols in place for credit card transactions is the use of encryption technology.
When a credit card transaction occurs, sensitive data is encrypted to prevent unauthorized access during the transaction process. Additionally, credit card networks employ fraud detection systems that monitor transactions in real-time. These systems analyze purchasing patterns and flag suspicious activity, providing another layer of security for cardholders.
Importance of CVV Codes and Expiration Dates
CVV codes and expiration dates serve a critical role in enhancing the security of credit card transactions. The CVV (Card Verification Value) is a three or four-digit number printed on the back or front of the card, and it is used to verify that the card is in the physical possession of the cardholder during online transactions. This extra step significantly reduces the chances of fraud, as even if someone obtains your credit card number, they would still need the CVV to complete a purchase.Expiration dates also contribute to security by ensuring that old cards cannot be used indefinitely.
Merchants are trained to request updated information when a card expires, which further protects cardholders from unauthorized transactions.
“The combination of CVV codes and expiration dates creates a formidable barrier against online fraud.”
Impact of Contactless Payment Technology on Credit Card Security
Contactless payment technology has transformed how credit card transactions are conducted, particularly in retail environments. This technology allows consumers to make purchases simply by tapping their cards on a payment terminal, which raises some important security considerations.One significant advantage of contactless payment is that it utilizes RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, which is designed to enhance security through encryption. Each transaction generates a unique code that cannot be reused, providing an extra layer of protection against fraud.
Furthermore, contactless cards typically come with built-in security features, such as anti-skimming technology, which prevents unauthorized scanning of card information.However, while contactless payments offer convenience and security, it is crucial for consumers to remain vigilant. Keeping cards secure and monitoring account statements for unauthorized transactions are essential practices, as the speed and ease of contactless payments can sometimes lead to unnoticed fraudulent activity.
“Contactless payment technology not only enhances user convenience but also integrates advanced security measures to protect card information.”
Vulnerabilities in Mobile Wallets: Mobile Wallets Vs Credit Cards – Which Is Safer For Online Payments
Mobile wallets have revolutionized the way we make transactions, offering convenience and speed. However, like any digital platform, they come with their own set of vulnerabilities that can expose users to security risks. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for anyone looking to use mobile wallets safely.One of the most significant concerns regarding mobile wallets is the wide array of threats and vulnerabilities they face.
While mobile wallets utilize advanced security features, they are not immune to risks. Users must remain vigilant about how they protect their devices and the sensitive information contained within their wallets.
Common Threats and Vulnerabilities
Mobile wallets can be targeted by various threats that compromise user security. Here are some notable vulnerabilities:
- Malware Attacks: Malicious software can infiltrate a mobile device, allowing cybercriminals to access sensitive wallet data.
- Unauthorized Access: If a device is not adequately secured, unauthorized individuals can gain access to the wallet, leading to potential theft.
- Data Breaches: Wallet service providers can experience data breaches, where user information and transaction details may be exposed.
- Device Theft: Losing a mobile device that contains a wallet can result in immediate financial loss if proper security measures aren’t in place.
Risks of Losing a Mobile Device
The loss of a mobile device poses a significant risk to users of mobile wallets. If a device is lost or stolen without adequate security measures, it can lead to unauthorized transactions and identity theft. To mitigate these risks, mobile wallet users should consider the following actions:
- Enable Remote Wipe: This feature allows users to erase data from their device remotely if lost.
- Use Strong Passwords: Securing the wallet with a strong password can provide an additional layer of security.
- Utilize Biometric Authentication: Features like fingerprint or facial recognition can prevent unauthorized access even if the device is in the wrong hands.
Phishing Attacks Targeting Mobile Wallet Users
Phishing attacks pose another serious threat to mobile wallet users. Cybercriminals often employ deceptive tactics to trick users into divulging sensitive information. These attacks typically occur through emails, text messages, or fake websites that appear legitimate.Key factors about phishing attacks include:
- Impersonating Trusted Entities: Attackers may impersonate banks or wallet providers to gain user trust.
- Links to Fake Websites: Users may be directed to fraudulent websites that mimic real ones, leading to data theft.
- Urgent Messages: Phishing attempts often create a sense of urgency, pressuring users to act quickly without verifying the source.
“Awareness of phishing tactics can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these attacks.”
Vulnerabilities in Credit Cards
Credit cards, while convenient and widely used for online transactions, are not without their vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks is crucial for users to protect themselves in the ever-evolving landscape of digital finance. A variety of threats exist that can compromise credit card security, leading to significant financial losses and identity theft.Credit card data breaches pose a serious risk to consumers and financial institutions alike.
When hackers infiltrate databases of companies that store credit card information, they can access sensitive data such as card numbers, expiration dates, and CVVs. These breaches can occur at any point in the transaction process, whether during online shopping or through compromised point-of-sale systems. The ramifications of such breaches are extensive, often resulting in fraudulent transactions, loss of trust, and significant financial repercussions for both the cardholder and the issuing bank.
Skimming Devices, Mobile Wallets vs Credit Cards – Which Is Safer for Online Payments
Skimming is a method used by criminals to capture credit card information without the cardholder’s knowledge. This process typically involves the use of a skimming device that can be discreetly attached to card readers at ATMs, gas stations, or retail locations. Here’s how skimming poses risks to credit card security:
Device Placement
Skimmers can be placed over legitimate card readers, making them almost indistinguishable to users. When a card is swiped, the skimmer records the data while the legitimate reader processes the transaction as normal.
Data Capture
The skimming device captures the magnetic stripe information from the credit card, allowing criminals to clone cards or create counterfeit versions.
Increased Vulnerability
With the proliferation of online shopping, stolen card data can be easily used for online purchases, leading to rapid and often irreversible losses for consumers.
“Skimming presents a hidden threat in everyday transactions, turning mundane purchases into potential gateways for fraud.”
Online Fraud Implications
The implications of online fraud for credit card users are severe, ranging from financial loss to damage to credit history. Online fraud can manifest in various forms, including phishing scams, where attackers deceive users into providing personal information, or through the use of stolen credit card details for unauthorized purchases.
Financial Loss
When credit card information is compromised, users may face fraudulent charges that can lead to significant financial loss, which can take time to recover.
Identity Theft
Stolen credit card information can lead to identity theft, where criminals open new accounts in the victim’s name, resulting in long-term financial damage.
Credit Score Impact
Fraudulent activity can negatively affect a cardholder’s credit score, making it more difficult to secure loans or other financial products in the future.
“The fallout from online fraud can linger long after the initial incident, impacting individuals’ financial health and peace of mind.”
In the world of digital transactions, it’s essential for credit card users to remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their information. Awareness of vulnerabilities, such as data breaches and skimming devices, can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to credit card fraud.
Comparing User Experience in Mobile Wallets and Credit Cards
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the convenience of payment methods greatly impacts consumer choices. Both mobile wallets and credit cards offer distinct user experiences that cater to different preferences and situations. Understanding these differences can help consumers make informed decisions about which payment method best suits their needs.Mobile wallets, such as Apple Pay and Google Wallet, provide a seamless payment experience through contactless technology and integration with smartphones.
This ease of use is appealing, especially in situations like grocery shopping or dining out, where a quick tap can finalize transactions. In contrast, credit cards, while slightly less convenient due to the physical card requirement, still offer reliable functionality, especially in online shopping or larger purchases where security measures like two-factor authentication may be employed.
Ease of Use and Situational Preference
The user experience associated with mobile wallets versus credit cards can vary based on the context in which they’re used. Here are some key points highlighting these variations:
- Speed of Transaction: Mobile wallets often allow for quicker checkouts, utilizing NFC technology for tap-and-go payments. For instance, at a coffee shop, a user can simply tap their phone to pay, whereas a credit card may require swiping or inserting a chip.
- Accessibility: Mobile wallets can be accessed directly from a locked phone through biometric authentication, making them convenient for on-the-go purchases. On the other hand, forgetting a physical credit card can cause inconvenience, especially if it’s needed for spontaneous expenses.
- Integration with Loyalty Programs: Many mobile wallets automatically integrate loyalty points and offers, enhancing the shopping experience. For example, using a mobile wallet at a grocery store might apply discounts automatically, whereas credit card loyalty points must typically be tracked manually.
Customer satisfaction levels also play a significant role in the preference for either payment method. Research shows that a majority of users find mobile wallets to be more user-friendly and efficient. Trust levels, however, can vary; some consumers express concerns regarding the security of mobile wallets due to the potential for phone theft or loss. In contrast, credit cards are often associated with established fraud protection policies, which can reassure users.
“Mobile wallets lead in convenience, while credit cards excel in customer trust.”
In conclusion, while mobile wallets can enhance the speed and ease of transactions, the established trust and familiarity of credit cards provide comfort for many users, particularly in online transactions. Ultimately, the choice between these payment methods often depends on individual preferences and situational needs.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
In the evolving landscape of digital payments, regulatory and compliance considerations are crucial for both mobile wallets and credit cards. As these payment methods become more prevalent, understanding the laws and regulations that govern them is essential for ensuring user security and trust. The payment ecosystem is subject to a variety of regulations that aim to protect consumers, promote transparency, and maintain the integrity of financial systems.
For credit card transactions, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is of utmost importance. This set of security standards is established to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. Compliance with PCI standards helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches and fraud, thereby protecting consumers’ sensitive information.
Regulations Governing Mobile Wallets and Credit Cards
Several regulations have a significant impact on how mobile wallets and credit card transactions are conducted. These regulations not only protect consumers but also establish frameworks for service providers.
- PCI DSS Compliance: As mentioned, PCI DSS is critical for credit card transactions. Organizations must adhere to its 12 requirements, which include maintaining a secure network, implementing strong access control measures, and regularly monitoring and testing networks.
- Electronic Funds Transfer Act (EFTA): This act provides guidelines for electronic transactions, ensuring consumers are protected from unauthorized withdrawals and requiring disclosures about fees and terms.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): This act mandates financial institutions, including mobile wallet providers, to explain their information-sharing practices to consumers and safeguard sensitive data.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): For mobile wallets operating in the EU, GDPR imposes strict rules on data collection and processing, emphasizing consumer privacy and control over personal data.
The importance of adhering to these regulations cannot be overstated, as non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
Specific Regulations Impacting Mobile Wallet Providers
Mobile wallet providers face unique regulations that address their operational frameworks and consumer interactions. These regulations are designed to adapt to the innovative nature of mobile payment systems while ensuring a high level of security and consumer protection.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Regulations: Mobile wallet providers are required to implement measures to prevent money laundering activities. This includes customer verification processes and monitoring suspicious transactions.
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) Regulations: In the U.S., the CFPB oversees consumer protection laws that mobile wallet providers must comply with, ensuring that consumers understand the terms of service and any associated fees.
- Local Regulations: Different countries or regions may have their own specific regulations for mobile wallets, such as licensing requirements or consumer protection laws, which can impact how these services operate.
Understanding and adhering to these regulatory frameworks is essential for mobile wallet providers to operate legally and maintain trust among their users. Compliance not only safeguards consumers but also enhances the overall security of the digital payment landscape.
Future Trends in Online Payment Security
As digital transactions evolve, so too does the landscape of payment security. With the increase in online shopping and digital wallet adoption, ensuring secure transactions has become paramount. This segment explores emerging technologies and trends that may revolutionize the safety of mobile wallets and credit cards.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Security
Several new technologies are on the horizon that could significantly enhance the security of online payments. These innovations aim to protect sensitive information and ensure safe transactions. Here are some key technologies to watch:
- Biometric Authentication: Technologies such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice recognition are gaining traction. These methods offer a higher level of security by tying payment authorization to unique biological traits.
- Blockchain Technology: While primarily associated with cryptocurrencies, blockchain’s decentralized ledger system provides an immutable record of transactions. This transparency can help reduce fraud and improve accountability in payment processing.
- Tokenization: This method replaces sensitive card information with a unique identifier (token) that is useless if intercepted. Tokenization helps minimize the risk of data breaches during online transactions.
- Quantum Computing: Though still in its infancy, quantum computing has the potential to create more secure encryption methods that can resist modern hacking techniques.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Payment Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is poised to transform the security landscape of online payments significantly. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, payment systems can analyze transaction patterns and detect anomalies in real-time, enhancing fraud detection capabilities. AI can also personalize security measures, adapting them to individual user behaviors. For instance, if a user typically makes purchases in a particular location, an attempt to process a transaction from a different country could trigger additional verification steps.
Furthermore, AI-driven chatbots can assist in customer service, helping users resolve transaction issues quickly, thereby improving overall security.
“AI systems are capable of processing vast amounts of data, making them invaluable in identifying potential threats before they can impact users.”
Shifts in Consumer Preferences Towards Payment Methods
Consumer preferences are shifting as more individuals become comfortable with digital payment methods. A significant trend is the growing reliance on mobile wallets due to their convenience and perceived security benefits. As younger consumers enter the market, they often prefer mobile wallets for their seamless integration with loyalty programs and ease of use.Traditional credit cards, however, still maintain a strong foothold, especially among demographics that favor established methods of payment.
Many consumers appreciate the consumer protections and fraud liability guarantees offered by credit card companies. Recent surveys indicate that up to 70% of consumers under 35 prefer mobile wallets for their transactions, while older generations may still lean towards credit cards due to familiarity and trust. This generational divide suggests a gradual evolution in payment preferences that could reshape the market.
“As technology continues to advance, understanding consumer behaviors will be crucial in predicting the future landscape of online payment security.”